
Uniting The Ledgers: Five Projects For Cross-Blockchain Compatibility
This article exampines five protocols for cross-blockchain interoperability: Wanchain, Komodo, Ark Ecosystem, POA Network and Polkadot.
In today’s blockchain industry, each blockchain project has unique a ecosystem of users, tokens and dApps. As a result, blockchain projects often operate in silos, each one separate from the others.
As the industry grows and progresses, interoperability between chains has become a new frontier for blockchain development.
Why Blockchain Interoperability is Necessary
Lack of interoperability has become a considerable hindrance for blockchain adoption. Without this connectivity, it’s impossible to transfer assets from one blockchain to another, and smart contracts are unable to interact with one another.
There are some solutions at the application level through companies like Crowd Machine, which offers a solution that easily incorporates the “interoperability of its apps with any blockchain.” However, this is not a decentralized solution.
What are Cross Blockchain Protocols and why are they needed?
Cross blockchain protocols are an emerging technology to allow value and information to move between different blockchains. They can settle transactions between different blockchains, using different consensus mechanisms while eliminating the need for third-party intervention.
Several emerging projects are attempting to develop platforms that can communicate with one another, without a third party intermediary. These projects include POA, Wanchain, Polkadot, Komodo, and Ark, among many others.
Wanchain
Wanchain is a cross-blockchain platform that seeks to create a “distributed bank” by connecting and exchanging value between different ledgers, to establish a decentralized financial infrastructure.
The protocol provides a framework for financial applications based on digital assets and cryptocurrencies. It’s also an independent blockchain network complete with support for its native coin, smart contracts, and dApps.
Wanchain’s goal is to provide financial services to all blockchain clients through their financial platform, through which any individual, firm, or institution can set up a business window to provide services. These services could include asset exchanges, credit payments, and transaction settlements.
Wanchain intends to interlink blockchains, with low transaction costs, and provide banking services to the unbanked. They also help others run their ledgers, smart contracts, and wallets through the Wanchain system.
The Wanchain protocol is currently live and offers cross-blockchain transactions with Ethereum, Bitcoin, and ERC20 tokens (such as DAI and MKR).
Polkadot
Polkadot is an inter-blockchain protocol that aims to allow independent blockchains to seamlessly transact and exchange information in a “trust-free” manner via multiple chains. The multiple chains provide a sort of a pooled security for each member of the network, regardless of the blockchain in which they operate.
The Polkadot protocol envisions itself as a complex multi-blockchain technology, with three key components: relay chains, parachains, and bridges.
The coordinated efforts of these three chains aim to allow for the protocol to process several transactions in parallel, making it easy to attain anonymity or formal verification.
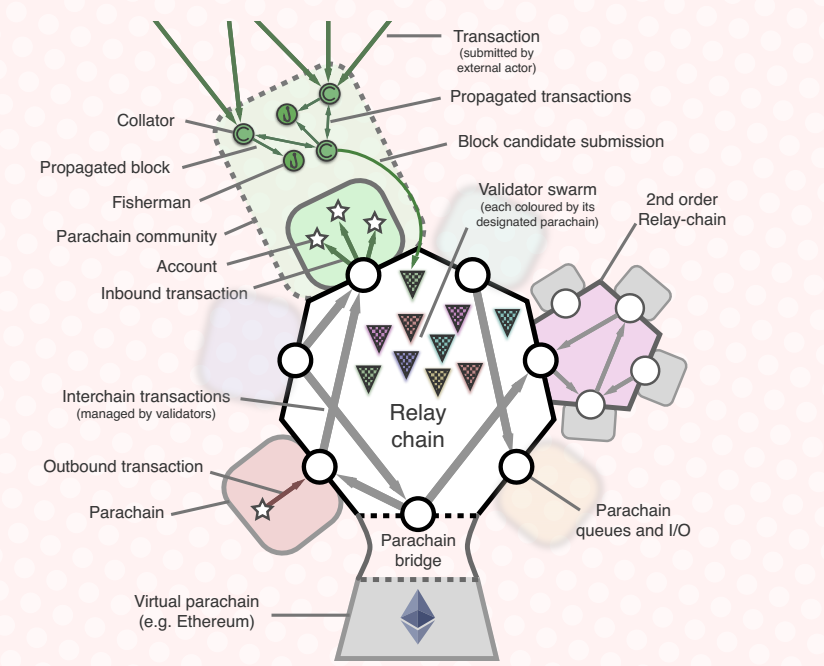
Each of these blockchains will seek to ensure that the Polkadot system remains secure, while adding the benefit of scalability through a common ecosystem for multiple blockchains.
The Polkadot project is still in development; it is expected to launch in Q3 of 2019, with planned compatibility with Bitcoin, Ethereum, Zcash, and other blockchains.
Ark
Ark is an open ecosystem with the primary purpose of increasing global blockchain adoption. It seeks to create an all-in-one blockchain solution that’s flexible, adaptable, and highly scalable, creating a “virtual spider-web of endless use cases.” Ark’s bridgechains can interact with any other blockchain, and provides several tools for users to create their own custom blockchains “within minutes.”*
The Ark network seeks to address the problem of poor blockchain adoption by providing projects with the ability to create, customize, and scale their blockchain networks. It uses a DPoS consensus algorithm, whereby users stake tokens to “vote” for 51 block-producing nodes. That makes entry to the network easy; unlike other DPOS systems, one only needs to stake some tokens, with no need to remain online in order to receive a share of block forging rewards.
The Ark protocol is live, with two-way transfers into Bitcoin, Litecoin and Ethereum. “You can even issue smart contracts on Ethereum directly from ARK without even touching Ethereum,” co-founder Travis Walker told us in an email. “It even calculates all fees and refunds any overage seamlessly.”
Komodo
Komodo is an open source platform that offers support for fungible, transparent, and private transactions. In 2018, the platform developed UTXO-based smart contracts, which can be implemented on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Komodo’s vision is to create a healthy, multi-blockchain ecosystem that enhances easy access and understanding of the technology. In addition to UTXO-based smart contracts, the platform boasts atomic swaps, scalability solutions, and interoperability solutions.
They’ve also launched some unique projects, like decentralized ICOs, and customizable “blockchain starter kits” that can be tailored to an individual client or enterprise’s requirements. Each chain in the ecosystem is interoperable with the Komodo main chain, through atomic swaps.
Currently, some aspects of the Komodo ecosystem are operational, such as their blockchain, consensus algorithm (Delayed Proof of Work), atomic swaps, and the Komodo token.
Other aspects, such as the Komodo’s developer portal and the custom consensus framework are still in the development phase.
Komodo provides cross chain compatibility with Bitcoin-protocol based coins, Ethereum, and Ethereum-based ERC20 tokens.
POA
The POA network is a fully decentralized permissioned blockchain that primarily focusses on the Ethereum protocol. It uses a Proof-of-Authority consensus algorithm through a network of nodes (known validators) and a governance-based penalty system.
The POA Network offers a cross-chain bridge to increase interoperability between protocols. With the bridge, platform users can transfer native POA tokens from the POA network to the Ethereum network. The POA20 standard has the exact characteristics of the ERC-20 token, and can be used on any platform with ERC-20 compatibility.
The POA blockchain is live and offers cross chain compatibility with Ethereum.
In a future of ever-increasing blockchain platforms, a few might stand the tests of market and time. For those platforms, interoperability will become an important function for survival in the future ecosystem. The ability to integrate and interact with each other appears to be a crucial necessity for global blockchain adoption.
*This section has been amended to reflect feedback from the ARK team.
The author is invested in digital assets, including Bitcoin and Ethereum, which are mentioned in this article.
