Decentralized Derivatives, The Beginner's Guide
Another area of finance waiting to get revolutionized

Share this article
Decentralized finance is flourishing. Lending platforms are still the most popular use case for DeFi, but decentralized derivatives are emerging as a contender for 2020. Here’s our guide to the major DeFi derivatives platforms.
Derivatives aren’t new to crypto. BitMEX opened the doors on its crypto futures trading platform back in 2014. Now, anyone wanting to trade crypto derivatives has plenty of exchanges to choose from, including Binance, OKEx, and Huobi.
Crypto derivatives operate in roughly the same way as traditional derivatives. A broker provides the contract and the leverage. Then, these contracts can be traded on exchanges. In the case of BitMEX and other crypto-derivatives platforms, it acts as both the broker and the exchange.
Decentralized derivatives are slightly different, in that they don’t require a broker. Instead, the terms of the contract can be programmed into smart contracts, eliminating the need for a third party. Settlement automatically takes place on-chain when the terms of the contract are fulfilled. The flexibility of decentralized derivatives is vast, enabling users to create instruments on virtually any underlying asset.
Decentralized derivatives account for around 18% of the total value locked in DeFi, according to DeFi Pulse. It’s the second most popular category of DeFi dApp after lending.
This guide provides an overview of the major DeFi derivatives platforms.
Synthetix
Synthetix started as a stablecoin protocol called Havven. In 2019, it rebranded and expanded its offering to include synthetic assets that track the value of real-world assets.
Since then, it’s been growing at a stellar pace. Currently, Synthetix is the most dominant decentralized derivative application by far, accounting for 98% of the value locked in DeFi derivatives, according to DeFi Pulse.
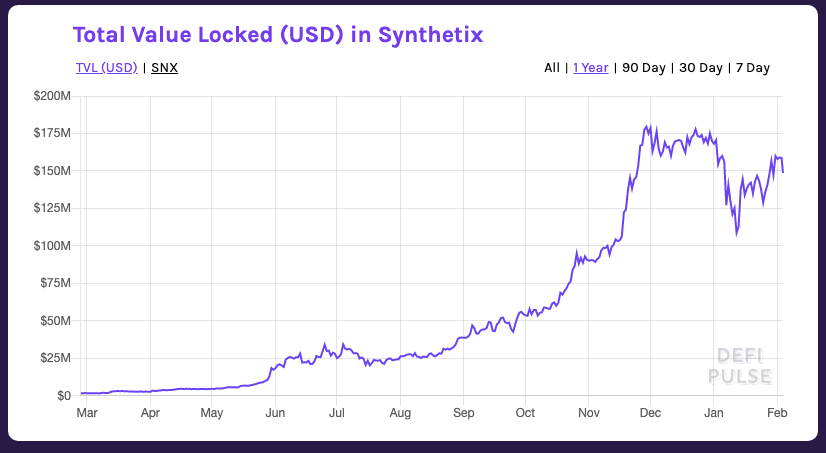
Synthetix allows anyone to stake its SNX token as collateral to mint the synthetic assets on its platform, known as Synths. Those who take the risk to mint these synthetic assets get rewarded in transaction fees on Synthetix’s decentralized exchange. This creates a positive feedback loop where people are incentivized to mint Synths to ensure their SNX tokens hold their value.
There are currently around 30 synthetic assets available for trading on the Synthetix platform, covering assets such as fiat currencies, cryptocurrencies, metals, and indices. In some cases, inverse Synths are also available, enabling traders to short assets. Price information is captured using Chainlink’s oracle service.
Despite its popularity, Synthetix hasn’t been without issues. In June last year, a trader using a bot managed to exploit an error in a price oracle, enabling the bot to convert a falsely inflated balance into the ETH Synth on the Synthetix platform. The trader in question returned the funds in exchange for a bug bounty.
Nexus Mutual
Nexus Mutual isn’t strictly a decentralized derivative platform—rather, it provides insurance coverage to those trading decentralized derivatives. It is a decentralized, community-owned insurance pool, enabling members to purchase insurance that provides coverage in the event of a smart contract failure. Conveniently, this covers decentralized derivatives operating on smart contracts.
The pool raised 12,000 ETH from participants in May last year. After fundraising the system was ready to start processing claims. Users must buy membership of the mutual for a nominal fee in ETH. After they’ve paid, members can buy insurance by paying into the pool with ETH, receiving NXM tokens in return.
NXM tokens enable members to vote on governance matters and to incentivize risk and claim assessments. Along with insurance and voting rights, members of Nexus Mutual are entitled to shares in any capital above what’s needed to settle claims.
Augur
The derivatives markets are essentially a more sophisticated form of gambling, providing traders with various instruments to speculate on the future value of an asset. Augur can be considered a kind of fusion between betting and derivatives. It’s a decentralized oracle and platform for prediction markets.
A prediction market simply means a place to buy and sell predictions or bets. Before Augur came along, these markets were only open to centralized parties like bookmakers or brokers, making them vulnerable to anti-gambling regulations. Now, anyone can open up a prediction market based on any real-world outcome. A concrete example could be betting on the price of Bitcoin reaching $20,000 before the end of 2020.
Using Augur, you could open up the market, and the value of your prediction will be priced according to users buying into it based on what’s happening in the real world. The value is always priced between 0 and 1 ETH, similar to betting odds in the dollar-denominated world
If the price of Bitcoin starts to rise, the YES predictions will be worth more, but if the price of Bitcoin falls, the NO predictions will increase in value. If Bitcoin hits $20,000 before the end of the year, then the value of your prediction is settled at 1 ETH, but if it gets to December 31 and Bitcoin hasn’t hit the price target, the prediction is settled with no payout to those who voted YES.
There’s a lot more going on under the hood, such as mechanisms for dispute resolution. But in summary, Augur’s decentralized prediction markets enable anyone to hedge against real-world events.
Started in 2014, Augur was among the first applications to be developed on Ethereum, and as such, was one of the earliest trailblazers in the DeFi movement. A second version of the software is due to be released in Q1 2020, which will integrate DAI and ZRX as settlement currencies, an off-chain scaling solution, and fiat onramps.
Other Projects to Watch
Given the vast potential of the decentralized derivatives markets, there are several other projects currently under development that are also worth watching.
Vega is a decentralized protocol for trading margined financial products. Participants will be able to create their own products, such as options and futures, using Vega’s “smart product” language.
The project secured $5 million in seed funding from investors led by Pantera Capital in October 2019. Vega is planning to operate as a layer 2 solution with Ethereum as the first available chain. However, the RSK Ecosystem Fund is one of the backers, implying that Bitcoin interoperability could also be on the horizon, given that RSK is a smart contract-enabled side chain of Bitcoin.
UMA is a decentralized platform enabling the creation of self-enforcing financial contracts. Any two parties can create a customized financial contract, specifying the terms, including margin requirements and termination conditions. UMA users can also take advantage of the UMA Synthetic Token Builder to create ERC-20 tokens that can track the value of anything.
CloseCross is developing a decentralized, multi-party derivatives trading platform. It aims to make it simple for anyone to enter the derivatives market by simply choosing an underlying asset, a prediction, and a time period. The platform operates a patented algorithm that increases the reward value for those assuming higher risk. CloseCross will also be available as a white-label solution, enabling anyone to set up a marketplace with their own branding and logo.
Watch This Space
The full potential of decentralized derivatives is only starting to unfold. But, given the data, it looks ready to explode in popularity this year. The Synthetix token alone has realized serious gains over the last twelve months, rising from $0.03 in January 2019 to over $1.10 at the time of writing. With new entrants poised to join and existing players continuing to innovate and expand, it’s definitely worth keeping both eyes on this burgeoning segment.
Revision Feb. 6, 2020, 14:30 CET: This article previously listed Veil, a second-layer Augur application. This was incorrect. Veil sunset its product in July 2019.
Share this article
